Day 31. Common Security Principles
CCNA Security 210-260 IINS Exam Topics
- 1.1.a Describe confidentiality, integrity, availability (CIA)
- 1.1.b Describe SIEM technology
- 1.1.c Identify common security terms
- 1.1.d Identify common network security zones
Key Topics
Today’s review focuses on the basic principles, concepts, and terminology of network security. First we will look at the three basic elements of network security and then examine some basic security terminology and the common security zones found in networks today.
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA)
The basic elements of network security are as follows:
- Confidentiality: Providing confidentiality of data guarantees that only authorized users can view sensitive information.
- Integrity: Providing integrity of data guarantees that only authorized subjects can change sensitive information. Integrity might also guarantee the authenticity of data.
- Availability: Providing system and data availability guarantees uninterrupted access by authorized users to important computing resources and data.
 Video 31.1—CIA
Video 31.1—CIA
SIEM
Security Information Event Management (SIEM) is a technology used in enterprise organizations to provide real-time reporting and long-term analysis of security events. SIEM provides user information (name, location), device information (manufacturer, model, OS version), and posture information (compliance, antivirus version, OS patches) for network security staff to quickly and accurately assess the significance of any security event. SIEM tools can aggregate data from many sources (routers, servers, firewalls), correlate the data into meaningful bundles, retain historical data for compliance and analysis, and provide real-time alerts when an attack is detected.
Common Network Security Terms
Table 31-1 lists some of the more common terms encountered in network security.
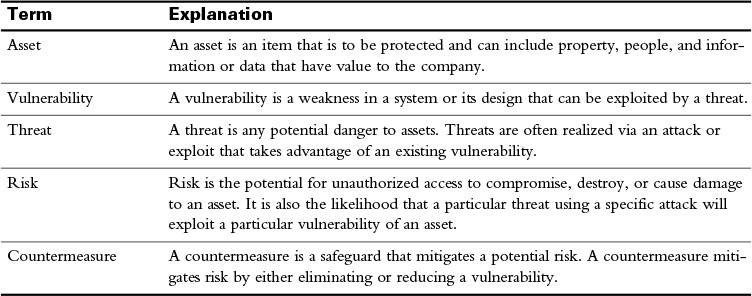
Table 31-1 Common Network Security Terms
 Activity: Identify Common Network Security Terms
Activity: Identify Common Network Security Terms
Security Zones
Before discussing the concept of security zones, it is important to understand the role of the firewall in network security. A firewall is a system that enforces an access control policy between two or more security zones. Although there are different types of firewalls, every firewall should have the following properties:
- It must be resistant to attack.
- All traffic between networks must flow through it.
- It must have traffic-filtering capabilities.
Firewalls commonly control access between the security zones that are based on packet source and destination IP address and port. Although firewalls can be placed in various locations within a network (including on endpoints), they are typically placed at the Internet edge, where they provide vital security.
The placement of the firewall allows for the creation of two basic security zones, as Figure 31-1 illustrates.
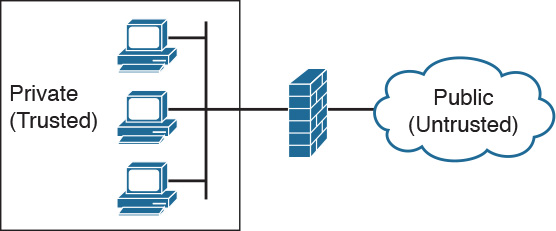
Figure 31-1 Security Zones
The public, untrusted network is commonly referred to as the “outside” security zone. This zone is fully outside the control of the organization. The private, trusted network is commonly referred to as the “inside” security zone. It is a zone in which systems owned by an organization reside and must be protected from systems that do not belong to the organization. Besides the inside and outside interfaces, it is typical to have at least one interface that is somewhere in between. This interface is often associated with a third zone called the demilitarized zone (DMZ), as shown in Figure 31-2. This zone usually contains a relatively small number of systems whose services are made available to systems residing in the outside zone. The DMZ devices, such as web servers, are owned and controlled by the organization, but they are accessed by systems outside of the organization’s control.
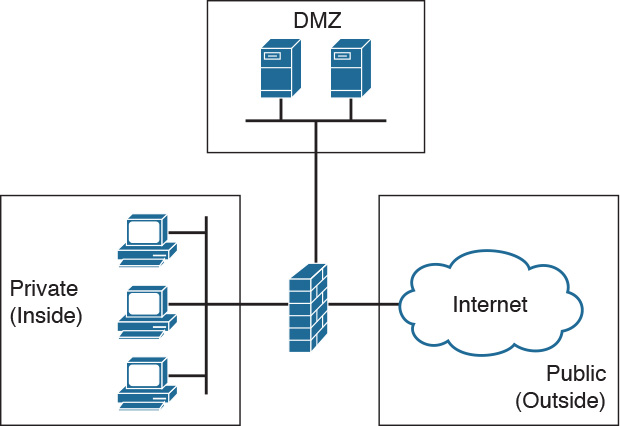
Figure 31-2 DMZ
Typically, the traffic flow between these three zones will be as described in Table 31-2.
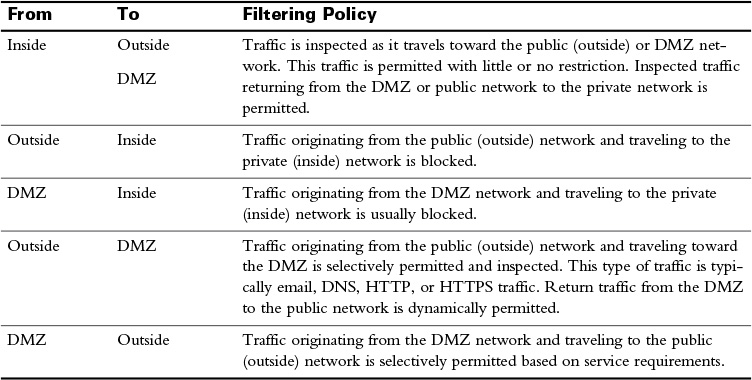
Table 31-2 Security Zone Filtering Policies
 Video 31.2—Security Zone Filtering Policies
Video 31.2—Security Zone Filtering Policies
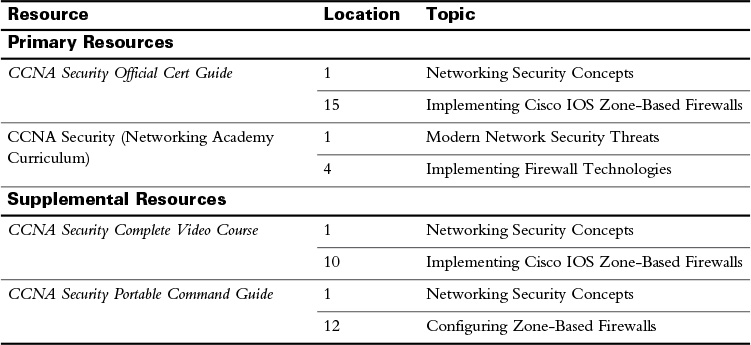
Study Resources
For today’s exam topics, refer to the following resources for more study.
 Check Your Understanding
Check Your Understanding